Explain Difference Between Mutation Rate and Neutral Mutation Rate
Sickle cell anemia overdominance in. An Introduction to General Organic and.

Difference Between Silent And Neutral Mutation Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
The neutral mutation rate is affected by the amount of neutral sites in a protein or DNA sequence versus the amount of mutation in sites that are functionally constrained.

. Examples would be exposure to chemicals or radiation. By quantifying these neutral mutations in protein andor DNA and comparing them between species or other groups of interest rates of divergence can be determined. Explain the difference between mutation rate and neutral mutation rate.
U_U_f_ neutral mutation rate. How can a mutation decrease the activity of a protein. Explain the difference between the mutation rate for a given nucleotide and the mutation rate for a given cell.
They can happen spontaneously when copying errors occur during cell division. In general fixation rates are lower in growing populations Waxman 2012. Under the neutral process mutation and genetic drift Neis genetic distance is linearly related to the time since divergence t ie.
Explain your bodys homeostatic control system response to this in terms of the four compon. This rate includes beneficial deleterious and neutral mutations. If the environment changes the mutation may be beneficial and it may help the organism adapt to the environment.
Mutation rates differ between species and even between different regions of the genome of a single species. The mutation rate is the frequency of all new changes to the DNA sequence over time. Explain How A Mutation Might Lead To Adaptation.
I expect that the average number of fixations to be equal to the average number of mutations in each generation or they converge over generations. The actual number of mutations in a given replication event will vary. Evolution is completely dependent on the generation of new variation.
Mutation is one of the major sources of variation that can lead to evolution. Because the neutral theory of Evolution by Kimura predicts that for neutral sites in the genome substitution rate is equal to the mutation rate. - 24071591 JonathanD9066 JonathanD9066 06172021.
For example mammals. The challenge of mutation rate estimation. This makes instinctive sense if you consider the single-generation fixation probability of a neutral allele which only exists at all but one copy in the.
The neutral mutation rate is affected by the amount of neutral sites in a protein or DNA sequence versus the amount of mutation in sites that are functionally constrained. Explain which types of selection patterns are being applied. To avoid this problem selective neutrality is sometimes enforced by the experimenter such that the number of mutations increases linearly with time 58 88.
Describe some ways in which DNA is altered to cause mutations. Explain the difference between the mutation rate and the neutral mutation rate. Mutations can also be induced by environmental factors or mutagens.
Which rate is likely to be greater for most genes and why. How a mutation might lead to adaptation. These different rates of nucleotide substitution are measured in substitutions fixed mutations per base pair per generationFor example mutations in intergenic or non-coding DNA tend to accumulate at a faster rate than mutations in DNA that is actively in use in.
Which rate is likely to be greater for most genes. Many mutations are neutral and remain in the population. Environmental factors may have an influence on the rate of mutation but they do not control what the mutation.
Most empirical analyses of neutral molecular clocks rely on the theorem that neutral mutation rates can be inferred from neutral substitution rates. The other explanation that has been given for the differences is the existence of substantial heterogeneity in mutation rates across the D-loop that is mutations occur preferentially at hypervariable sites from our data half of the reported mutations displayed above-average site-specific mutation rates and the other half were detected at. It is believed that neutral mutations mutations that have neither a positive or negative effect accumulate at a exponential rate over time.
Mutations can occur in two ways. Struggle with what is meant by a particular mutation rate. Fixation rates for neutral alleles are affected by changes in population size given a constant mutation rate.
Accounting for variation in mutation rates Of course we rarely expect the mutation rate per individ-ual per year to be equal in different populations or species which means that empirical estimates of the N eRR for neutral mutations may not be flat. Difference between the neutral substitution rate and the mutation rate. Under genetic drift probability of fixation of an allele is equal to its _____ in the population.
-Rate of acquiring a resistance mutations μr of beneficial sites in the genome 67167 x per nucleotide mutation rate 54x10-10 μr 12x10-7per genome replication lamB and malT are giant targets in the genome causing the rate of lambda resistance to be many orders of magnitude higher than the per nucleotide mutation rate. In general deleterious mutations tend to be eliminated and hence are less likely to be sampled than neutral ones introducing a bias in mutation rate estimates. University of California - Los Angeles.
Explain the difference between mutation rate and neutral mutation rate. The organisms that survive pass this favorable trait on to their offspring. Mutation occurs at the individual level while evolution is change at the population level that occurs over many generations.
Because mutation is the ultimate source of all variation both adaptive and deleterious a mechanistic understanding of the evolutionary process will be incomplete until a detailed account has been made of the rate of origin molecular nature and phenotypic consequences of spontaneous alterations for a diversity of organisms. Rather than indicating that there will always be a 10 difference between the ancestor and offspring a 10 mutation rate means that each site in the genome independently has a 10 chance of changing during replication. By quantifying these neutral mutations in protein andor DNA and comparing them between species or other groups of interest rates of divergence can be determined.
Answer 1 of 27. However when corrected for gender assuming that the mutations present in men have the same evolutionary weight of somatic mutations because they will inevitably be lost and for the probability of intraindividual fixation the value for the mutation rate obtained for HVRI and HVRII 02415 mutationssiteMyr was in the upper end of the. Neutral mutations on the other hand are changes in DNA sequence that have no direct effect.

What Is Neutral Mutation What Does Neutral Mutation Mean Neutral Mutation Meaning Youtube

Neutral Theory From Molecular Evolution To Community Ecology Fangliang He Department Of Renewable Resources University Of Alberta Ppt Download

Evolutionary Genetics Charles Darwin Darwin S Theory Of Evolution Through Natural Selection 1 Principle Of Variation Among Individuals Within Any Population Ppt Download
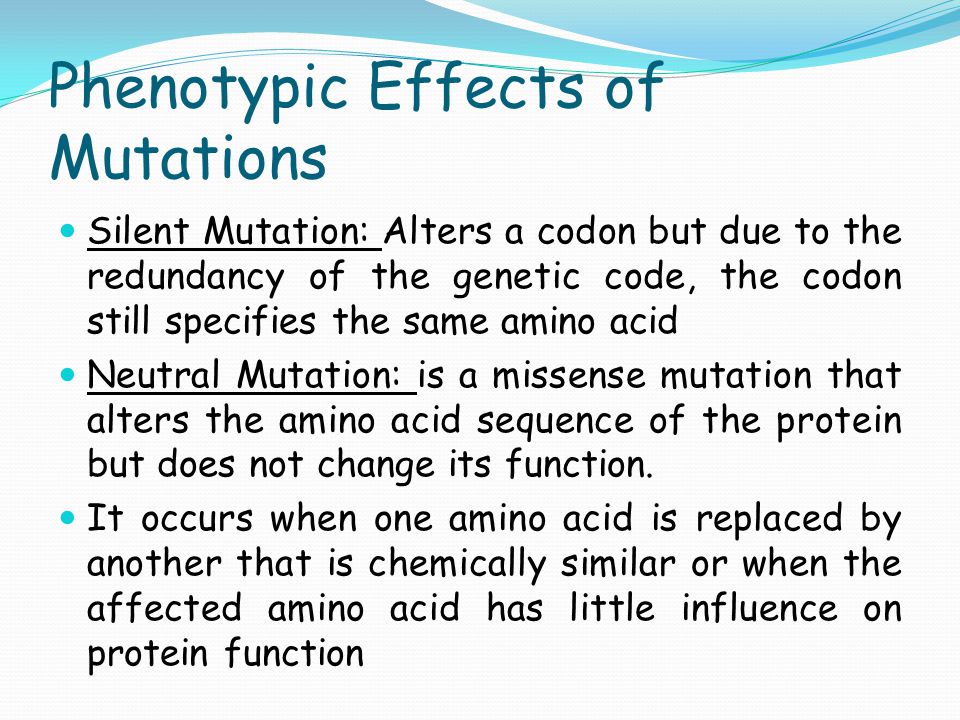
Gene Mutations Ppt Video Online Download

Difference Between Silent And Neutral Mutation Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
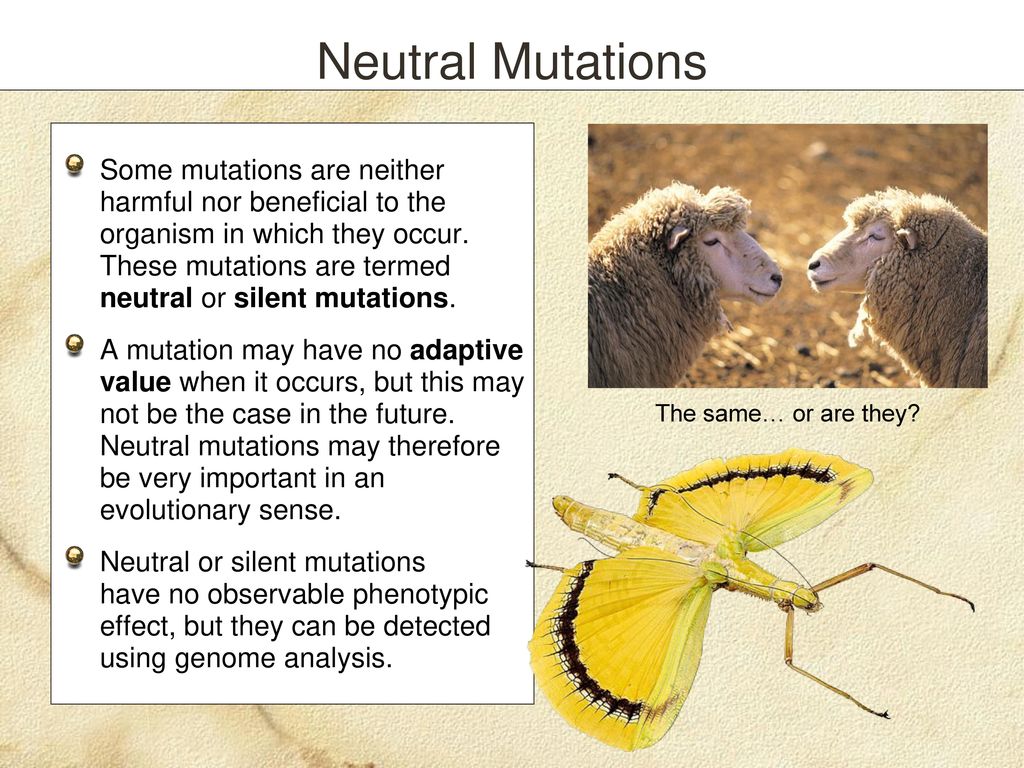
Adaptation Selection Ppt Download

Genetic Mutations What Is A Mutation What Are Some Examples Of Harmful Mutations Neutral Mutations Are What Are Some Examples Of Beneficial Mutations Ppt Download

What Are The Significance Of Neural Mutation In Speciation What Are The Evidence Any Experimental Research Design

Mutations What Is A Mutation A Mutation Is

Mutation Rate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

4 2 Mutations A Gene Mutation Involves A Change In The Order Of Bases A C T G That Make Up The Gene There Are Several Types Of Gene Mutation A Gene Ppt Download

Genetic Mutation Learn Science At Scitable
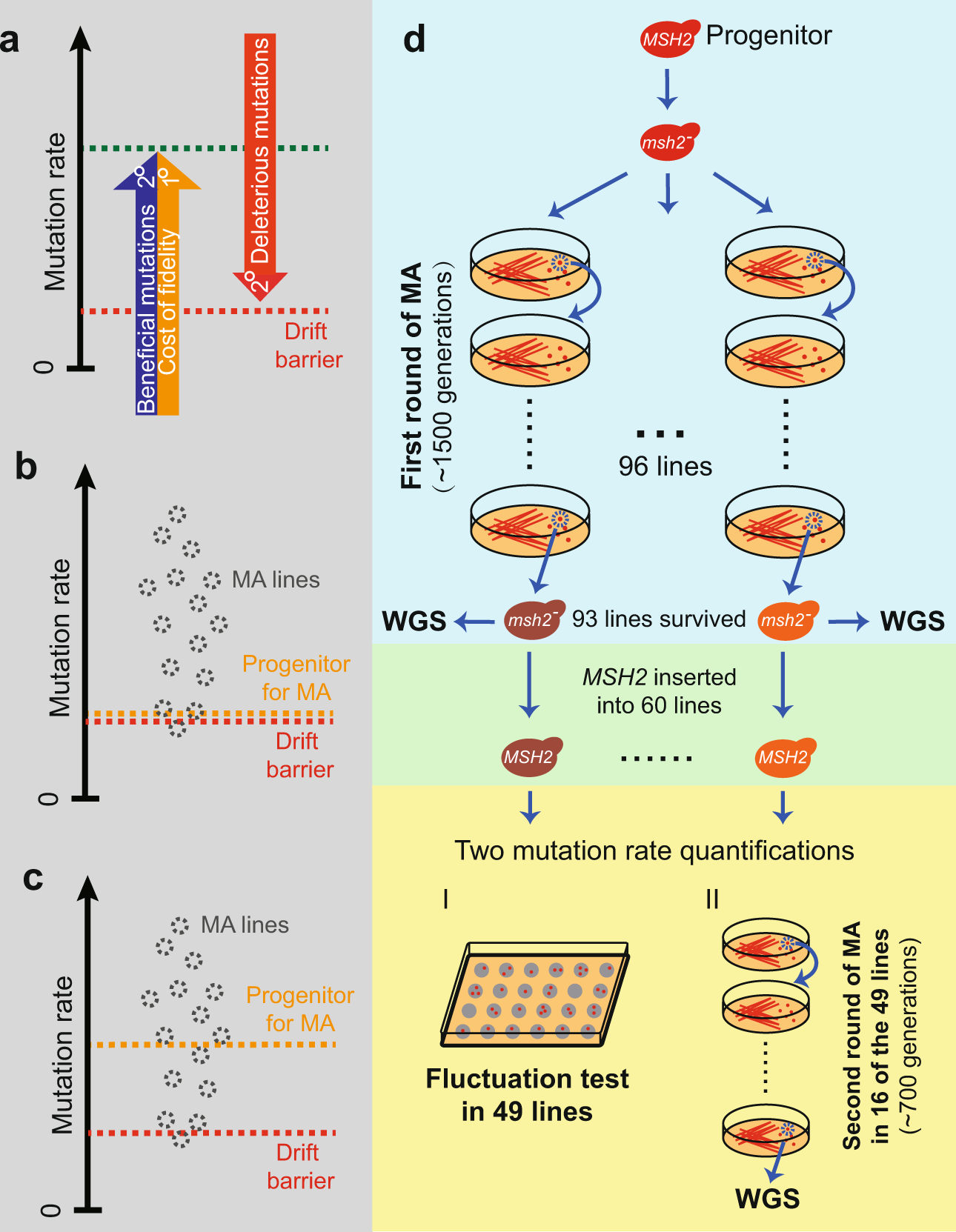
The Rate And Molecular Spectrum Of Mutation Are Selectively Maintained In Yeast Nature Communications

Warm Up Discuss The Role That Mutations Play In Evolution Ppt Download

Neutral Theory The Null Hypothesis Of Molecular Evolution Learn Science At Scitable

Derivation Of The Relationship Between Neutral Mutation And Fixation Solely From The Definition Of Selective Neutrality Pnas

Mutations What Are They How Do They Occur What Causes Them Ppt Download


Comments
Post a Comment